Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 174

Modeling Day and Night
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 1 of the PDF), learners make a "mini-globe" to investigate the causes of day and night on our planet.
Tiny Tubes
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make "totally tubular" forms of carbon. Learners use chicken wire to build macro models of carbon nanotubes.

Avalanche
Source Institutions
In this geology activity, learners create a model using a mixture of salt and sand inside a CD case. When the case is tilted or inverted, the mixture dramatically sorts into a layered pattern.

Fan Cart
Source Institutions
If a sailboat is stranded because there is no wind, is it possible to set up a fan on deck and blow wind into the sail to make the boat move?

Water Body Salinities I
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the different salinity levels of oceans, rivers and estuaries.
Modeling Limits to Cell Size
Source Institutions
This investigation provides learners with a hands-on activity that simulates the changing relationship of surface areas-to-volume for a growing cell.
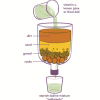
Water Clean-up
Source Institutions
This is an activity (located on page 3 of the PDF under Water Clean-up Activity) about the use of reduction agents to decontaminate ground water.
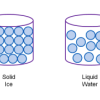
Atoms and Matter (3-6)
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build models of atoms and molecules, then consider their role in different phases of matter, density, and mixtures and solutions.

Water Body Salinities II
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discuss the different salinities of oceans, rivers and estuaries.
Space Stations: Bones of Contention
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make models representing bones on Earth and bones that have been in space. They discover what happens to bones without proper exercise and nutrition.

Landing the Rover
Source Institutions
In this team design challenge (page 19-24 of PDF), learners "land" a model Lunar Rover in a model Landing Pod (both previously built in activities #3 and #4 in PDF).

Jell-O Model of Microfluidics
Source Institutions
This activity uses Jell-O(R) to introduce learners to microfluidics, the flow of fluids through microscopic channels.

The Pull of the Planets
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model the gravitational fields of planets on a flexible surface.

Space Stations: Sponge Spool Spine
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners simulate what happens to a human spine in space by making Sponge Spool Spines (alternating sponge pieces and spools threaded on a pipe cleaner).

Dunking the Planets
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners compare the relative sizes and masses of scale models of the planets as represented by fruits and other foods.

Sled Kite
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a sled kite that models a type of airfoil called a parawing.
Going for a Spin: Making a Model Steam Turbine
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how various energy sources can be used to cause a turbine to rotate.

Why Doesn’t the Ocean Freeze?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how salt water freezes in comparison to fresh water.

Glue Stick Sunset
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore why the sky is blue. Learners model the scattering of light by the atmosphere, which creates the blue sky and red sunset, using a flashlight and clear glue sticks.
Polymers are Chains (K-2)
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make a paper model of a polymer, then make Silly Putty, an actual polymer.
