Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 90

Cleaning with Dirt
Source Institutions
Learners build a filter from old soda bottles and dirt. They create polluted water, and pour it through their filter to clean it.

Acid (and Base) Rainbows
Learners use red cabbage juice and pH indicator paper to test the acidity and basicity of household materials. The activity links this concept of acids and bases to acid rain and other pollutants.
Mercury in the Environment
Source Institutions
In this environmental science lesson, learners will examine the dangers of mercury and how humans contribute to growing mercury emissions on Earth.
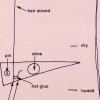
Better Hair Through Chemistry
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners hook up a hair to a lever system and create a hair hygrometer to measure changes in humidity.

A Funny Taste
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the different salinities of various sources of water by taste-testing.

Water Body Salinities I
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the different salinity levels of oceans, rivers and estuaries.

Fragile Waters
Source Institutions
In this activity (on pages 18-29) learners explore the impact of the March 24, 1989 oil spill in Alaska caused by the Exxon Valdez tanker.
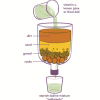
Water Clean-up
Source Institutions
This is an activity (located on page 3 of the PDF under Water Clean-up Activity) about the use of reduction agents to decontaminate ground water.

Acid Rain Effects
Learners conduct a simple experiment to model and explore the harmful effects of acid rain (vinegar) on living (green leaf and eggshell) and non-living (paper clip) objects.

What's Hiding in the Air?: Acid Rain Activity
As a model of acid rain, learners water plants with three different solutions: water only, vinegar only, vinegar-water mixture.

Composting
Source Institutions
In this environmental science activity, learners research what is essential for plant life and the necessary components of soil to support plants.

Why Doesn’t the Ocean Freeze?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how salt water freezes in comparison to fresh water.

Do the Mystery Samples Contain Life?
Source Institutions
In this activity (on pages 13-16 of the PDF) learners investigate three mystery samples to see which one contains life. The three samples are sand, sand and yeast, and sand and antacid.

The Carbon Cycle and its Role in Climate Change: Activity 3
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the human influences on the carbon cycle and examine how fossil fuels release carbon.

Amazon Water Cycle Roleplay
Source Institutions
In this creative roleplay activity, learners will explore the various processes of the water cycle using movement, sound, and props to aid in comprehension.

What is Light?
Source Institutions
In this four-part activity, learners will discover the exciting world of light--the most important form of energy in our world--and be able to identify and describe different types of light.

Does Sunscreen Protect My DNA?
Source Institutions
In this laboratory experiment, learners explore how effectively different sunscreens protect yeast cells from damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
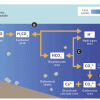
Coral, Carbon Dioxide and Calcification
Source Institutions
In this group activity, learners act out key stages of the "ocean carbon cycle" (also known as the "carbonate buffer system") through motions, rearranging blocks and team tasks.
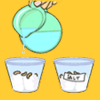
Salt, Soil and Seeds
Source Institutions
Discover how the salt in soil affects plant growth with a few seeds, some cotton, and salt. In this hands-on activity, you will plant seeds in 2 different kinds of soil, containing more or less salt.

What's In Your Breath?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners test to see if carbon dioxide is present in the air we breathe in and out by using a detector made from red cabbage.
