Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 37

Lava Layering: Making and Mapping a Volcano
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how geologists use stratigraphy, the study of layered rock, to understand the sequence of geological events.

Hot Equator, Cold Poles
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use multiple thermometers, placed at different angles, and a lamp to investigate why some places on Earth's surface are much hotter than others.
Amazing Albedo
Source Institutions
In this experiment, learners work in teams to investigate how the color of a surface influences its ability to reflect light and therefore heat.

Earth's Energy Cycle: Albedo
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners experiment and observe how the color of materials that cover the Earth affects the amounts of sunlight our planet absorbs.

The Four Seasons
Source Institutions
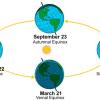
In this lesson that includes hands-on activities and demonstrations, learners discover that it is the tilt of the Earth's axis (not its proximity to the sun) that causes the seasons.

Moonlight Serenade
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners act as the Earth and observe how different angles between the Sun, Earth, and Moon affect the phases of the moon we see each month.

Weather Stations: Temperature and Pressure
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the relationship between temperature and pressure in the lower atmospheres of Jupiter and Earth.

Understanding Albedo
Source Institutions
In this activity related to climate change, learners examine albedo and the ice albedo feedback effect as it relates to snow, ice, and the likely results of reduced snow and ice cover on global temper
Recipe for a Moon
Source Institutions
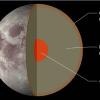
In this activity, learners discover that the Moon, like Earth, is made up of layers of different materials. Learners work in teams to make models of the interiors of the Moon and Earth.

My Angle on Cooling: Effects of Distance and Inclination
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover that one way to cool an object in the presence of a heat source is to increase the distance from it or change the angle at which it is faced.

Exploring the Solar System: Stomp Rockets
Source Institutions
In "Exploring the Solar System: Stomp Rockets," participants learn about how some rockets carry science tools—not scientists—into space, and how a special kind of rocket called "sounding rockets" can
What's the Angle?
Source Institutions
This activity helps learners understand how the angle of the Sun affects temperatures around the globe.

Solar Water Heater
Learners work in teams to design and build solar water heating devices that mimic those used in residences to capture energy in the form of solar radiation and convert it to thermal energy.
The Shadow Knows I
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will measure the length of their shadow from the Sun and compare it three to four months later.

House Warming
Source Institutions
In this physical sciences activity, learners explore how passive solar design increases energy efficiency.
The Return of El Nino
Source Institutions
In this activity related to climate change and data analysis, learners examine temperature and precipitation data to determine if climate variations are due to El Niño.

Freezing Lakes
Source Institutions
In some parts of the world, lakes freeze during winter. In this activity learners will explore water’s unique properties of freezing and melting, and how these relate to density and temperature.

The Shadow Knows II
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will measure the length of a shadow and use the distance from the equator to calculate the circumference of the earth.

Weather Stations: Winds
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a toaster to generate wind and compare the appliance's heat source to Jupiter's own hot interior. Learners discover that convection drives wind on Jupiter and on Earth.
Weather Stations: Phase Change
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe the water cycle in action! Water vapor in a tumbler condenses on chilled aluminum foil — producing the liquid form of water familiar to us as rain and dew.
